NeuroVISNEUROTRANSMITTERS ANALYTIC
Blood-Brain Barrier Permeation Test
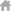 > 시험안내 > Blood-Brain Barrier Permeation Test
> 시험안내 > Blood-Brain Barrier Permeation Test
Blood-Brain Barrier Permeation
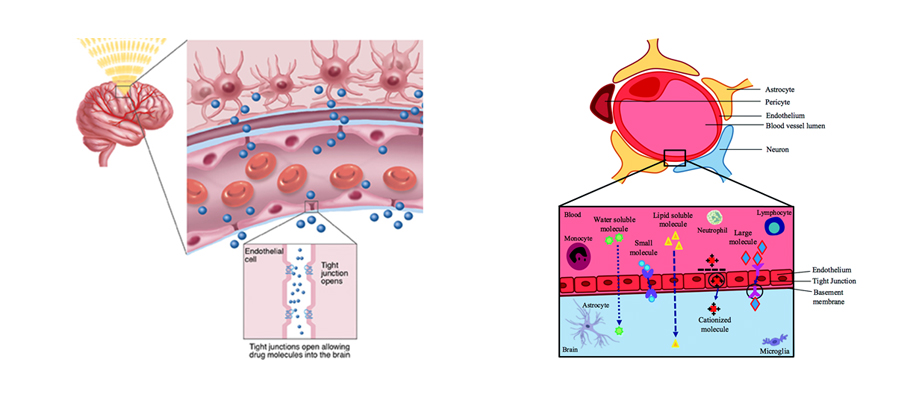
- Blood-brain barrier (BBB) is a specialized barrier that protects the brain microenvironment from toxins and pathogens in the circulation and maintains brain homeostasis.
- The principal sites of the barrier are endothelial cells of the brain capillaries whose barrier function results from tight intercellular junctions and efflux transporters expressed on the plasma membrane. This function is regulated by pericytes and astrocytes that together form the neurovascular unit
Necessity
- Several neurological diseases such as stroke, Alzheimer's disease, brain tumors are associated with an impaired BBB function.
- Assessment of the BBB permeability is therefore crucial in evaluating the severity of the neurological disease and the success of the treatment strategies employed.